View Providers
Routine screenings help doctors detect colon cancer early on—even before you develop symptoms. That's important because colon cancer caught early on is usually easier to treat.
Doctors use several procedures to screen and test for colon cancer. Many screenings involve an exam of your rectum and colon. Doctors can also test your stool for signs of cancer.
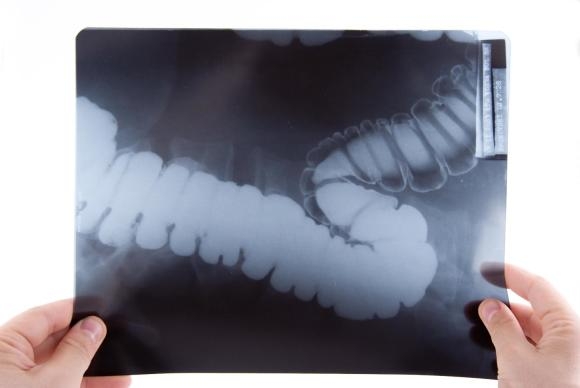
Barium Enema (Lower GI Series)
A barium enema involves a series of X-rays of your large intestine and part of your small intestine. Together, they make up the lower gastrointestinal (GI) tract.
These X-rays can reveal several problems, including:
- Colon polyps
- Hernias
- Tumors
- Ulcers
For this test, a contrast liquid fills your lower intestine. The liquid contains barium, a silver-white metallic compound. It makes it easier to see abnormal areas on X-rays.
A similar test is a double-contrast barium enema. It uses contrast liquid and air to outline the inside of your colon and rectum. These X-rays show a greater level of detail and can reveal smaller abnormalities in the large intestine. Suspicious growths require more testing, such as a colonoscopy.
Sigmoidoscopy
This test examines your rectum and sigmoid, which is the lower part of your colon. The test uses a thin tube called a sigmoidoscope. It includes a light and a tiny camera. A doctor puts the tube into your rectum. A monitor displays images from the camera. These images show any abnormal growths.
The tube used in this procedure is about two feet long. Doctors can see the entire rectum but less than half of the colon. The tube may also have a tool to remove small polyps. Doctors examine these samples for signs of cancer.
This test lasts 10 to 20 minutes. It is not painful. Most people do not need sedatives.
Colonoscopy
A colonoscopy allows doctors to examine the entire colon and rectum. Doctors use a longer thin tube, called a colonoscope. There's also a light and camera on it. Doctors put the scope through the rectum and into the colon. A monitor displays images of the colon. Special tools may be passed through the tube to remove abnormal growths or tissue samples.
You need to prepare for this test by emptying your colon and rectum so your doctor can see their inner linings during the test. This can be done several ways. It usually involves drinking a laxative the night before and the morning of the procedure. You may not eat or drink anything else after midnight the night before.
You are sedated for this test. The test itself lasts about 30 minutes, but it may take longer if your doctor needs to remove a growth.
Virtual Colonoscopy (CT Colonography)
Virtual colonoscopy is an advanced CT (computed tomography) scan of your colon and rectum. Regular X-rays create a two-dimensional image, like a basic photograph. A CT scan creates a three-dimensional view of your colon and rectum.
A CT scanner takes a series of pictures of your colon. You lie still on a table as the scanner rotates around your body. A computer puts these images together. These detailed images reveal any abnormal growths on the lining of the colon.
A drawback of this test is that doctors cannot remove any cell (tissue) samples or growths. If you have polyps or other abnormalities, you will need a separate procedure, such as a sigmoidoscopy or colonoscopy.
Fecal Occult Blood Test
This test detects blood in the stool. Blood vessels on the surface of large polyps or cancers are usually fragile. When you pass stool, these blood vessels can break or bleed tiny amounts of blood. For the test, doctors check a small sample of your stool. They're testing for blood that’s invisible to the naked eye.
It can be unnerving to have a cancer screening test, but keep in mind these types of tests are your best chance of preventing colon cancer. Your doctor can remove polyps during colonoscopy. Also, if your doctor finds a small cancerous tumor in the beginning stages, it may be possible to remove it during colonoscopy.